
RANGE OF SERVICESGlaucoma Outpatient Clinic |
|
Our Glaucoma Outpatient Clinic performs the following tests: Testing visual acuity Testing anterior segment of the eye Measuring intraocular pressure Gonioscopy (to distinguish between open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma) Pachymetry (the measurement of corneal thickness) Testing the field of view Measuring retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness by the HD OCT Zeiss Cirrus
What is glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a set of eye diseases in which the optic nerve is damaged in a characteristic pattern. This can permanently damage vision in the affected eye(s) and lead to blindness if left untreated. According to Ministry of Health and Glaucoma Protection Association in Poland 67mln people are affected by glaucoma in the world and 6mln is blind because of that.
How does glaucoma develop?
Glaucoma is the gradual loss of nerve cells in the eye, mainly caused by raised eye pressure. This occurs when fluid outflow becomes obstructed over time, so that the correct amount of fluid cannot drain out of the eye. Glaucoma generally develops when eye pressure increases and it starts pressing on nerve fibers mechanically and causes its atrophy. Another theory that explains glaucoma development is impairment of nerve fiber feeding and oxygen deficiency which is a result of persistent blood vessel spasm or blood circulation impediment in vessels transporting blood to optic nerve in case of atherosclerosis. Aoxic nerve atrophies and blindness develops.
What are the symptoms of glaucoma?
The symptoms of glaucoma depend on the type of the angle. Open-angle glaucoma affects 80% of patients. The eye’s drainage canals become clogged over time, causing an increase in internal eye pressure and subsequent damage to the optic nerve. There are typically no early warning signs or painful symptoms of open-angle glaucoma. It develops slowly and sometimes without noticeable sight loss for many years. Most people who have open-angle glaucoma feel fine and do not notice a change in their vision at first because the initial loss of vision is of side or peripheral vision, and the visual acuity or sharpness of vision is maintained until late in the disease. By the time a patient is aware of vision loss, the disease is usually quite advanced. The remaining 20% of the patients suffer from closed-angle glaucoma. In this type the rise in pressure is rapid, the symptoms also occur suddenly. Understandably, people who are experiencing acute angle-closure glaucoma are extremely uncomfortable and distressed as the symptoms include severe eye pain, nausea and vomiting, headache, blurred vision and/or seeing haloes around light (because the cornea is swollen).
How to treat glaucoma?
Glaucoma is treated pharmacologically, by laser or by the use of surgery.
What does pharmacological treatment mean?
It involves direct eye medications (eye drops) as well as systemic use medications.
Glaucoma direct eye medications: - prostaglandins - help the fluid in the eye flow out by opening alternative drainage canals(e.g. Xalatan) - Beta-blockers (also known as beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents) – help the fluid of the eye flow out and influence its production (e.g. Timoptic, Oftensin, Betoptic) - carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – reduce the production of the fluid in the eye (e.g. Trusopt, Azopt) - adrenergic receptor agonists – for open-angle glaucoma to reduce the production of the fluid in the eye and help it to flow out (e.g. Brimonidine, Oftanex) - complex effect medications (Fotil, Cosopt) - parasympaticomimetics – used in certain cases causing the pupil to contract (e.g. Pilocarpina, Izoptocarbachol)
Systemic use medications:
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - reduce the production of the fluid in the eye, used in a form of tablets (Diuresin) or by intravenous infusion (Diamox) - hyperosmotic drugs – decrease eye pressure by reducing the amount of fluid due to plasma osmolality changes. Administered orally (Glicerol) or intravenously (Mannitol).
What does the laser treatment look like?
YAG laser treatment of closed-angle glaucoma means making a cut in the iris which improves the flow of the fluid. SLT laser treatment brings satisfactory effects in open-angle glaucoma.
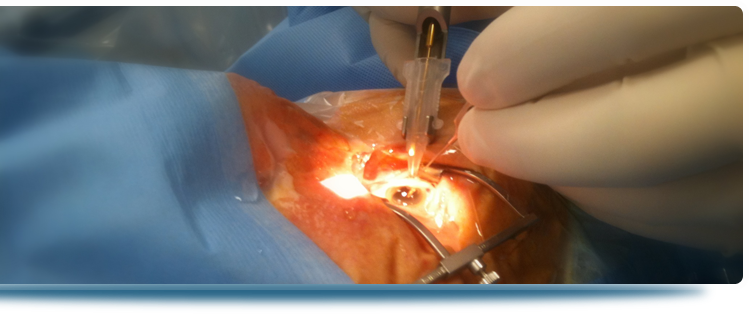
What is the use of surgery in glaucoma treatment?
For closed-angle glaucoma the surgery means cutting out the iris or the trabeculectomy which is removing part of the eye's trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures. The efficiency of eye surgery is really high. |
number of visitors: 969232 OCULUS Eye Diseases Treatment Center | 3 Feliksa Nowowiejskiego Street | 75-587 Koszalin
design: internet-media.pl
